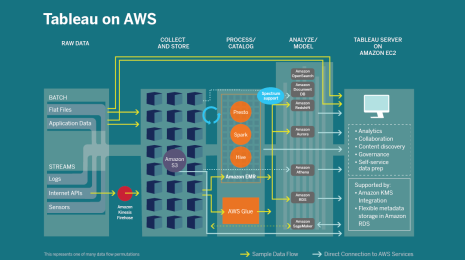
Enabling SQL analysis with Tableau and Amazon Aurora
It's the end of the quarter, and your team has been busy closing deals all week. You need to know how close you are to meeting quota, but there's a problem.
The extracted data set you use updates nightly, and it doesn't have today's closed deals included. You'd connect to your SQL database, but it's locked down to protect write operations. You're flying blind, and it's all because your database can't reliably serve the analytics needs of your company while also storing and collecting data.
The situation above will be familiar to many of you. At most organizations, the SQL database is sacrosanct. Day in and day out, DBAs protect the write operations and storage requirements of the database to ensure that no matter what, every piece of data is accurately recorded for posterity.
Analysis? In most cases, analysis can wait. Extracts can be scheduled at slow times of the day like the early morning. Live connections to the database during business hours (when business users actually have questions) are dangerous and unnecessary. Unfortunately, this limits the usefulness of the data that is being so carefully stored and curated.
At least that was the case until recently. With Amazon Aurora (and its read replicas), Tableau users can connect directly to the database to perform any kind of analysis they want, at any time they want, without affecting or harming the write operations on the main database.
How Tableau and Aurora work together
Read replicas are essentially independent endpoints in an Aurora DB cluster devoted to read operations. You can distribute up to 15 across three Availability Zones within the AWS region that the database utilizes. A single reader end-point provides access to the read replicas. All read requests are load-balanced across all the read replicas in an Aurora cluster, helping to ensure that no one read replica becomes overloaded serving up the analytical needs of your company.
Read replicas are highly useful for direct connectivity with Tableau because they allow the analyst to drag-and-drop any field or produce any query without wondering what the effect will be on the database itself. Tableau’s optimized connector produces SQL that is pre-optimized for Aurora, resulting in efficient and direct SQL that will optimize performance automatically.
What’s more, Tableau users can create hierarchies, folders, groups, calculations, and modify the aliases of any field to help clean and curate data. You can publish that metadata definition to Tableau Server along with the direct connection to the Aurora read replica. This lets you effectively save a single version of the truth that anyone can connect to and use at will—as long as they have permissions, of course.
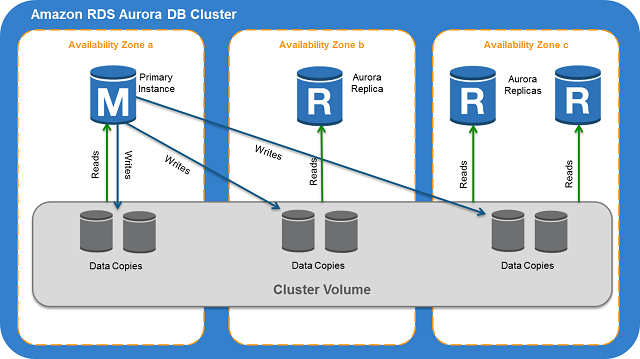
Read replica architecture in Aurora
Tableau Server also allows embedded permissions to rely upon the row-level permissions you’ve already set in your Aurora instance. Or you can set that level of permission for any view, workbook, folder, or group on Tableau Server itself. With this level of specificity in permissioning, you can be sure only the right people can view sensitive data and do so without any trouble or friction.
In short, Tableau and Aurora are a powerful combination that can free your organization from the restraints of analysis with most SQL databases. That means no more waiting to analyze data, or waiting for extracts to update; just direct, secure, and efficient connectivity to Aurora, and drag-and-drop visualizations and easy sharing.
If you’d like to see Tableau and Aurora in action, join us on Nov. 2 for an in-depth webinar and demo.
Verwante verhalen
Subscribe to our blog
Ontvang de nieuwste updates van Tableau in je inbox.